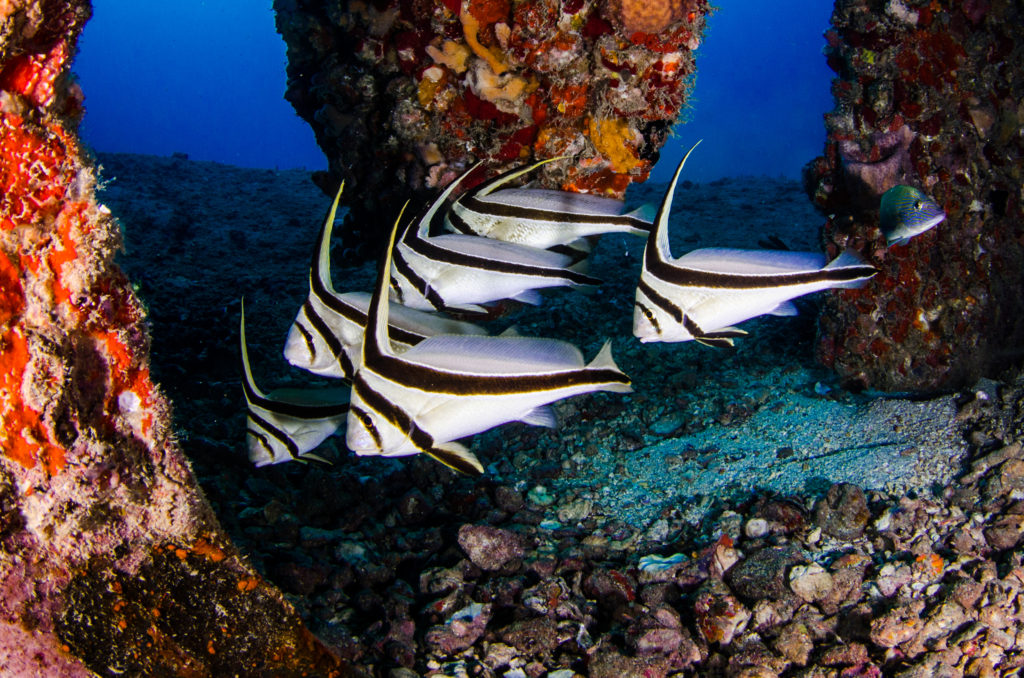
The classic bullseye rash of Lyme
Just like last year, experts are predicting more Lyme disease. While it used to be a pesky disease only in our midatlantic/Lyme Connecticut area of the world, Lyme continues to appear across the northeast and has been reported on the west coast of the United States. According to the American Academy of Pediatric’s Redbook, about fifty percent of reported Lyme disease is during June and July. We’ve already had children come to our office with tick bites concerns, so here’s an update:
Lyme disease is spread to people by blacklegged ticks. Take heart- even in areas where a high percentage of blacklegged ticks carry the bacteria that causes Lyme disease, the risk of getting Lyme from any one infected tick is low. Most of the little critters DON’T carry Lyme disease… but there are an awful lot of ticks out there. Blacklegged ticks are tiny and easy to miss on ourselves and our kids. In the spring, the ticks are in a baby stage (nymph) and can be as small as a poppy seed or sesame seed. To spread disease, the tick has to be attached and feeding on human blood for more than 36 hours, and engorged.
In areas in the United States where Lyme disease is prevalent (New England and Mid-Atlantic states, upper Midwest states such as Minnesota and Wisconsin, and California), parents should be vigilant about searching their children’s bodies daily for ticks and for the rash of early Lyme disease. Tick bites, and therefore the rash as well, especially like to show up on the head, in belt lines, groins, and armpits, but can occur anywhere. When my kids were young, I showered them daily in summer time not just to wash off pool water, sunscreen, and dirt, but also for the opportunity to check them for ticks and rashes. Now that they are older I call through the bathroom door periodically when they shower: “Remember to check for ticks!” Read our post on how to remove ticks from your kids.
“I thought that Lyme is spread by deer ticks and deer are all over my yard.” Nope, it’s not just Bambi that the ticks love. Actually, there are two main types of blacklegged ticks, Ioxdes Scapularis and Ioxdes Pacificus, which both carry Lyme and feed not only on deer, but on small animals such as mice. (Fun fact: Ioxdes Scapularis is known as a deer tick or a bear tick.)
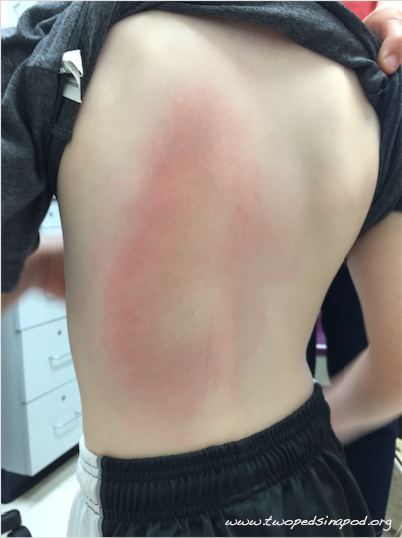
Most kids get the classic rash of Lyme disease at the site of a tick bite. The rash most commonly occurs by 1-2 weeks after the tick bite and is round, flat, and red or pink. It can have some central clearing. The rash typically does not itch or hurt. The key is that the rash expands to more than 5 cm, and can become quite large as seen in the above photo. This finding is helpful because if you think you are seeing a rash of Lyme disease on your child, you can safely wait a few days before bringing your child to the pediatrician because the rash will continue to grow. The Lyme disease rash does not come and then fade in the same day, and the small (a few millimeters) red bump that forms at the tick site within a day of removing a tick is not the Lyme disease rash. Knowing that a rash has been enlarging over a few days helps us diagnose the disease. Some kids have fever, headache, or muscle aches at the same time that the rash appears.
If your child has early localized Lyme disease (just the enlarging red round rash), the diagnosis is made by having a doctor examine your child. Your child does not need blood work because it takes several weeks for a person’s body to make antibodies to the disease, and blood work checks for for antibodies against Lyme disease, not actual disease germs. In other words, the test can be negative (normal) when a child does in fact have early localized Lyme disease.
Other symptoms of early Lyme disease may accompany the rash or can occur even in the absence of the rash. This stage is called Early Disseminated disease. Within about one month from the time of the tick bite, some children with Lyme develop a rash that appears in multiple body sites all at once, not just at the site of the tick bite. Each circular lesion of rash looks like the rash described above, but usually is smaller. Additional symptoms include fever, body aches, headaches, and fatigue without other viral symptoms such as sore throat, runny nose, and cough. Some kids get one-sided facial weakness. Blood testing at this point is more likely to be positive.
The treatment of early Lyme disease is straightforward. The child takes 2-3 weeks of an antibiotic that is known to treat Lyme disease effectively such as amoxicillin or doxycycline. Your pediatrician needs to see the rash and evaluate other symptoms to make the diagnosis. Treatment prevents later complications of the disease. Treated children fortunately do not get “chronic Lyme disease.” Once treatment is started, the rash fades over several days and other symptoms, if present, resolve. Sometimes at the beginning of treatment the child experiences chills, aches, or fever for a day or two. This reaction is normal but you should contact your child’s doctor if it persists for longer.
Later stages of Lyme disease may be treated with the same oral antibiotic as for early Lyme but for 4 weeks instead of 2-3 weeks. The most common symptom of late stage Lyme disease is arthritis (red, swollen, mildly painful joint) of a large joint such as a knee, hip, or shoulder. Some kids just develop joint swelling without pain and the arthritis can come and go.
For some manifestations, IV antibiotics are used. The longest course of treatment is 4 weeks for any stage. Again, children do not develop “chronic Lyme” disease. If symptoms persist despite adequate treatment, sometimes one more course of antibiotics is prescribed, but if symptoms continue, the diagnosis should be questioned. No advantage is shown by longer treatments. Some adults have lingering symptoms of fatigue and aches years after treatment for Lyme disease. While the cause of the symptoms is not understood, we do know that prolonged courses of antibiotics do not affect symptoms.
For kids eight years old or older, if a blacklegged tick has been attached for well over 36 hours and is clearly engorged, and if you live in an area of high rates of Lyme disease-carrying ticks, your pediatrician may in some instances choose to prescribe a one time dose of the antibiotic doxycycline to prevent Lyme disease. The study that this strategy was based on and a few other criteria that are considered in this situation are described here. Your pediatrician can discuss the pros and cons of this treatment.
Bug checks and insect repellent. Protect kids with DEET containing insect repellents. The Centers for Disease Control recommends 10 to 30 percent DEET- higher percent stays on longer. Spray on clothing and exposed areas and do not apply to babies under two months of age. Grab your kids and preform daily bug checks- in particular look in crevices where ticks like to hide such as the groin, armpits, between the toes and check the hair. Ticks can be tough to spot. Dr. Lai once had a elementary school patient who had a blacklegged tick in the middle of his forehead. The mother noticed it at breakfast, tried to brush it off, thought it was a scab and sent the boy to school. Later that day the teacher called saying, “I think your son has a bug on his face.”
Misinformation about this disease abounds, and self proclaimed “Lyme disease experts” play into people’s fears. While pediatricians who practice in Lyme disease endemic areas are usually well versed in Lyme disease, if you feel that you need another opinion about your child’s Lyme disease, the “expert” that you should consult would be a pediatric infectious disease specialist.
For a more detailed discussion of Lyme disease, look to the Center for Disease Control website: www.cdc.gov.
Julie Kardos, MD and Naline Lai, MD
©2017, 2016, 2009 Two Peds in a Pod®