
Questions: Why does that child run into the road? Why does that child hit other kids?
Answer: Because no one ever taught him not to.
Toddlers need lots of teaching, so where do you start? To help teach your on-the-move, act-first-and-ignore-the-consequences toddler how to become more civilized, first make sure BOTH parents agree on the rules. Teach your toddler that you mean what you say. When you call your toddler and he does not come right away, GO TO HIM AND LEAD HIM BY THE HAND OR PICK HIM UP no matter what the situation. Also remember that civilizing a toddler is a work in progress, not an afternoon project.
These are negative behaviors we want to train out of our toddlers: hitting, kicking, biting, pinching, and in any way inflicting pain on others. Excitement and anger are normal reactions in toddlers, but these negative responses to excitement or anger are always unacceptable.
Before we go further let’s review normal toddler behavior. These are things that you just can’t punish a toddler for, but rather you can try to capture on camera and to enjoy the memory later:
- Making a mess. All toddlers are messy. They can’t help it. They don’t have the fine motor coordination to prevent dropping food or for keeping toys contained to one area. (I am recalling with a smile a home-movie of my twin toddlers double-fisting a spaghetti dinner). Besides, to a toddler (and to many adults for those of you who used to watch Dave Letterman) it’s always fun to watch things splat on the floor. That being said, kids are never too young to teach “clean-up.” Make it fun and light-hearted, not onerous. All kids love to use brooms, so encourage them to help clean up the Cheerios that coat the floor after a meal.
- Touching everything. They will touch themselves and others- they are just curious.
- Speaking their minds. Toddlers are truthful and literal, not malicious or insinuating. My oldest son at age 3 saw a man with one arm and said very loudly, “Look, Mommy, that man has only one arm!”
How to discipline:
Catch ’em being good. This works wonders if you are consistent about it. Be specific about your praise. Tell your toddler, “I like how you are not hitting your brother right now,” or “Good job playing quietly while your baby sister naps,” or “Great job putting the legos away in the box!” instead of “You are being good now.”
Teach consequences: If he throws a toy, say “NO throwing that toy,” and take the toy away for a minute or two to make your point.
Chastise the behavior, not the child. Say to your child “No hitting,” not “You are bad for hitting.”
First make it clear that a behavior is not acceptable. Toddlers are not mind readers. If you never told her, “Don’t rummage through the garbage can,” she will not know better.
Parents need to be on the same page. Discuss in advance, not in front of your child, what the consequences are for misbehavior. If one parent”gives in” to a tantrum and one does not, your toddler will become confused, then anxious, and then learn how to pit parents against each other. He will throw longer, louder, more destructive tantrums because he knows, if he hangs on long enough, ONE person will give him what he wants.
Have immediate consequences. Avoid “Wait until your mom gets home.” Also avoid “When we get home from the store, you are in trouble.” As determined as they can get, toddlers also paradoxicaly have the attention span and memory of a flea. However, in order to give an appropriate, immediate consequence, plan your consequence before you need it or else you may give out one that you regret.
For example, if you and your toddler are having a fine time at the playground with other parents and their toddlers, you may regret this warning: “Stop hitting Billy with your toy car or we will leave the playground.” If your child ignores you, then you are stuck leaving the playground. And leave, you must! If you fail to heed your own warning, your toddler will learn that you do not mean what you say. He will see you as a wimp and will always try to take advantage of you. A better way to stop your kid is to say, “Stop hitting Billy with your toy car or I take that car away from you.” Then take it away if he continues the behavior. Here are the benefits:
1-Teach your child that you mean what you say.
2- Protect others from your toddler’s dangerous behavior.
3- Preserve your own sanity. Why should you have to miss out on talking to other mommies while enjoying the day with your toddler? Sure, your toddler may tantrum in response to his lost car, but after the tantrum your toddler and you can continue to have fun at the park.
Don’t nag. Toddlers are professionals at ignoring parental nagging. Just follow through on your consequence for failure to obey you.
Ignore whining. Whining is very hard to stop once you allow your toddler to get what he wants when he whines. Instead, ignore his whining and nagging (just as your toddler does so easily and naturally when you do it to him). Only grant him your attention when he uses his regular voice. Tell him once: “I can’t understand when you talk that way. I only understand your Joey (insert your child’s name here) voice.” Then ignore him until he uses his “regular” voice.
Catch teachable moments. If you see another toddler misbehaving OR behaving well, point out the behavior to your toddler. You could say, “Oh, she hit her sister. I am so glad you are not hitting now. You know that our rule is No Hitting!” Also use books to point out desirable behavior. Plenty of books that you read to your children have examples of children having fun together or working toward a goal together without hitting, biting, or kicking each other. Point that out!
Time out and its permutations:
Time-out is a consequence. The goal of time-out is to stop the undesirable behavior and to give negative associations to the bad behavior.
The traditional way of giving a Time-out in response to an aggressive or otherwise inappropriate behavior is to place your child in a chair or stool or on the floor in a corner or other quiet, boring place in the house for one minute per age of the child. Try not to use a spot which is associated with relaxation and sleep such as his crib.
Time-out is more of a mental place than a physical place. Years ago when I was out with Dr. Lai and our kids, her then 18-month-old hit her 3-year-old sister. Dr. Lai firmly told her 18 month old, “NO hitting, Mommy is not talking to you for one minute!” and she turned her back and folded her arms, making it a point of not looking at her daughter (Of course I was there to make sure her 18- month-old didn’t run into trouble). Her 18-month-old had a tantrum but she got the message.
My own twins were a handful- often they would bite or hit each other over a toy that they both wanted. Rather than attempting to put two twins in two Time-Out chairs, I put the TOY in time-out on top of the refrigerator, where they could see it but not reach it, for the number of minutes of my twins’ age. Yes, I had to endure a double tantrum but the undesirable behavior, namely the hitting, stopped. Over time they learned to think twice about hurting each other. Read more about twin toddler discipline tips here.
Teaching self-calming is different from disciplining misbehavior/unsafe activities.
Your kids may throw tantrums often in response to your discipline. This is perfectly fair. Toddlers are allowed to feel frustrated and angry (“If you’re happy and you know it clap your hands; if you’re angry and you know it throw a fit!”). Just ignore the tantrum and remove any breakables from the line of fire. The goal is for your child to have a bad feeling about making a bad choice. If she has a tantrum, she may later remember that if she throws a toy at someone, it will be removed from her and She Will Feel Bad about it. We will give you more tips about helping to stop an endless tantrum in our next post. Remember, though, that once time out is over, it is over. Move on and don’t continue to talk about the incident.
We do not recommend hitting your toddler as punishment or as a way to stop them from some undesirable behavior. Toddlers mirror your behavior. They will pretend to swipe a smart phone. They will blow kisses back to you. Toddlers will suddenly will start spewing inappropriate words because they hear their parents using those words. So, be on your best behavior. If you hit your child, you will model hitting as a proper response for anger. Try not to hit your child even in jest. You don’t want to be explaining to other parents on the playground that your hitting child “doesn’t know better.”
Be aware it will feel like you are reiterating the same teaching points endlessly You will often feel you are talking to yourself. Even though you told a toddler once not to rummage through a garbage can, you’ll have to repeat the instructions the next time you see a different garbage can. As my brother-in-law says,”You don’t ever stop. Kinda like practicing layups or free throws in basketball.”
Remember to take a deep breath: It is easy to lose control of yourself when you spend a lot of time with a toddler because toddlers, even though they are all adorable, can be infuriating, unreasonable, and irrational. Remember who is two and who is thirty-two. You NEED to be in control. If not, give yourself a timeout.
If you find a day with your toddler particularly tough, just do what melted my heart when my boys were toddlers. When asked, “Who will you marry?” they would always say “YOU, Mom.”
Julie Kardos, MD and Naline Lai, MD
©2015 Two Peds in a Pod®
Based on our original 2009 podcast about toddler discipline- you can listen to it here.





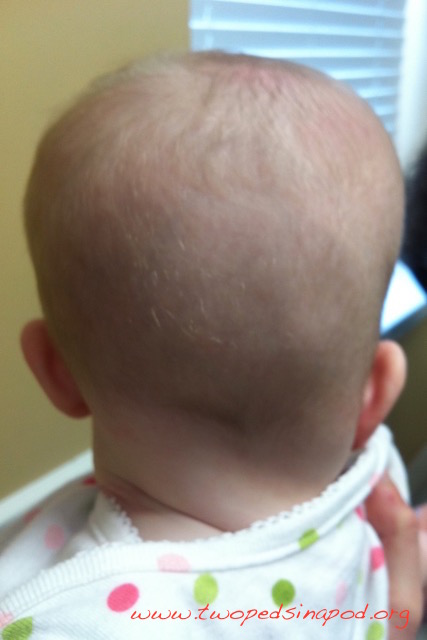 Squeezed through the birth canal, many babies are born with pointy, cone-shaped heads. Others, delivered by caesarian section, start off life with round heads. Few babies begin with a flat head. But as parents put babies on their backs to sleep in accordance with
Squeezed through the birth canal, many babies are born with pointy, cone-shaped heads. Others, delivered by caesarian section, start off life with round heads. Few babies begin with a flat head. But as parents put babies on their backs to sleep in accordance with 

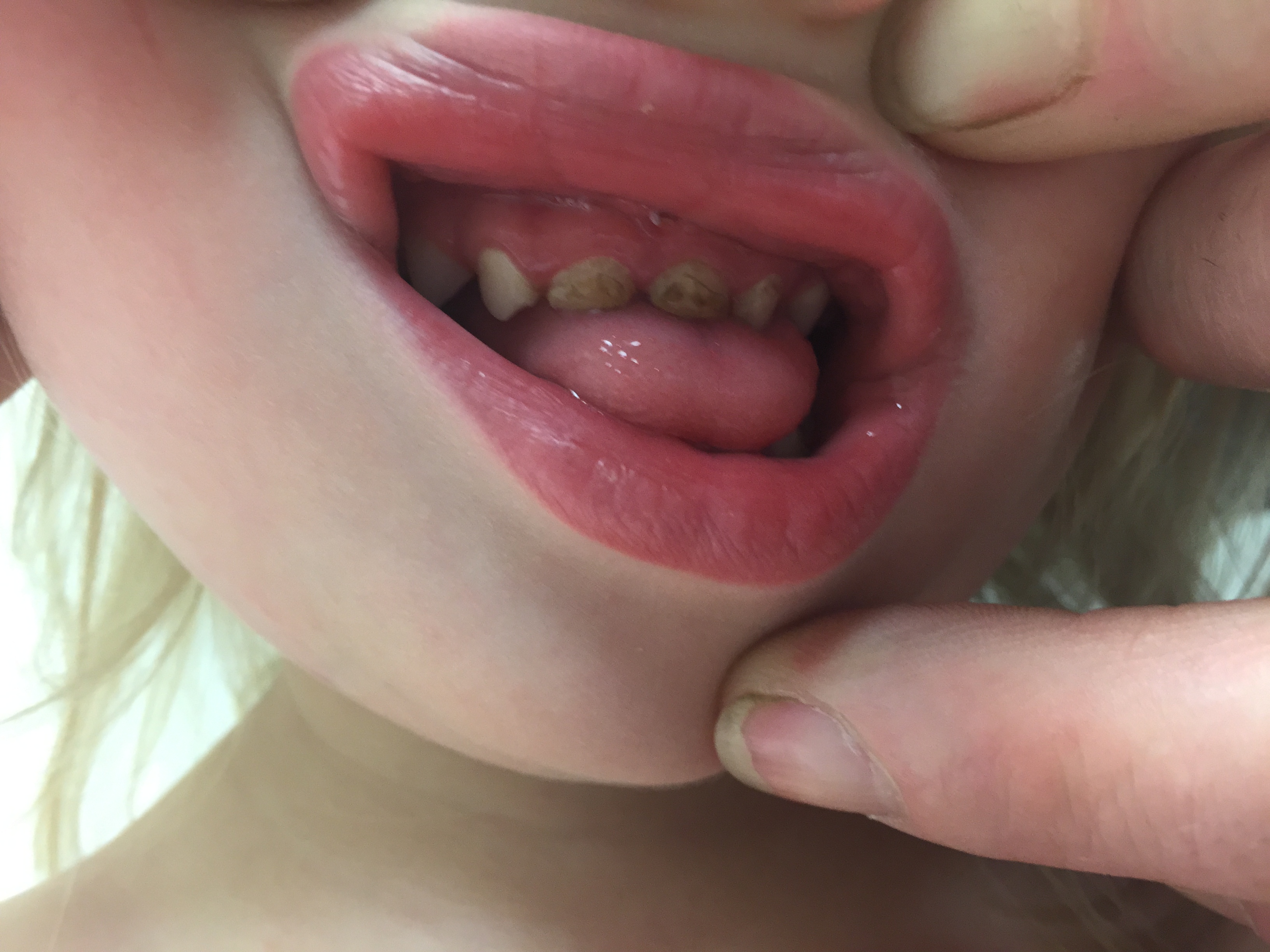 This drives us crazy: Listed on many pediatric developmental milestone charts, there is the six month milestone, ” can hold their own bottle. ” Unfortunately, this is the last thing we want our patients to do. Babies who feed by holding their own bottle tend to suck for a longer period of time than when they are at the breast or when a parent holds the bottle. Prolonging the time any sweet substance, whether breast milk, cow’s milk, or watered down juice is in the mouth can produce cavities. Even in toothless babies, the sugar can seep through gums and rot the teeth producing cavities called “bottle rot” in the two front teeth. As shown above, sucking on a sippy cup constantly can also produce the characteristic damaging pattern and cause rotten teeth.
This drives us crazy: Listed on many pediatric developmental milestone charts, there is the six month milestone, ” can hold their own bottle. ” Unfortunately, this is the last thing we want our patients to do. Babies who feed by holding their own bottle tend to suck for a longer period of time than when they are at the breast or when a parent holds the bottle. Prolonging the time any sweet substance, whether breast milk, cow’s milk, or watered down juice is in the mouth can produce cavities. Even in toothless babies, the sugar can seep through gums and rot the teeth producing cavities called “bottle rot” in the two front teeth. As shown above, sucking on a sippy cup constantly can also produce the characteristic damaging pattern and cause rotten teeth.

 As your kids apply to college or return home from college for winter break, we urge you to keep in mind an alarming, yet typical scenario which involves binge drinking that student health physicians encounter on a too-frequent basis–Drs. Kardos and Lai.
As your kids apply to college or return home from college for winter break, we urge you to keep in mind an alarming, yet typical scenario which involves binge drinking that student health physicians encounter on a too-frequent basis–Drs. Kardos and Lai.